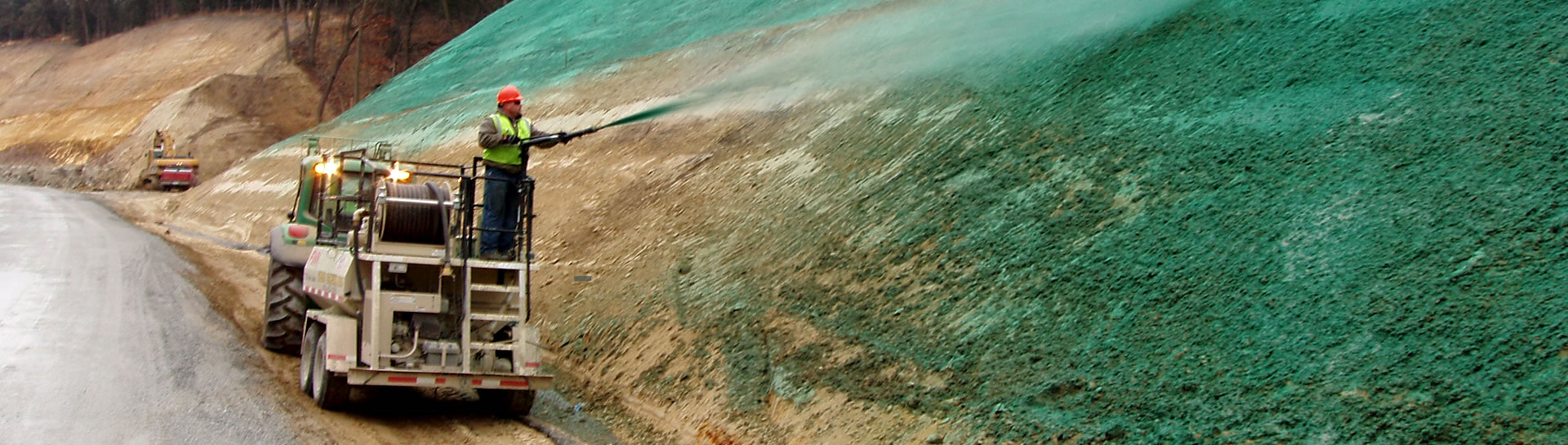
Erosion Control and Vegetative Establishment
The hydraulically applied product provides immediate erosion protection while creating an environment that assists in accelerating vegetative establishment. Vegetation then provides the long term erosion protection while improving site aesthetics and acting as a filter to remove sediment and other undesirable storm water constituents from entering receiving water bodies.
When evaluating hydraulic technologies, the following properties are most relevant when attempting to achieve optimum erosion control and vegetative establishment:
- Functional Longevity
- Percent Effectiveness
- Vegetative Establishment
- Shear Stress
Hydraulically applied materials are combinations of wood and wood cellulose fibres and water, with or without the addition of tackifiers, stabilizing emulsions, flocculating agents and man-made fibres. These ingredients are mixed in hydroseeding equipment and sprayed onto disturbed soil surfaces to protect from wind and water erosion. They can be applied without seed for temporary erosion control or with seed, fertilizers and soil amendments for permanent or temporary vegetative establishment.
There are four main types of hydraulically applied materials that are grouped together based on similar performance properties:
- Hydraulic Mulch
- Stabilized Fibre Matrix
- Bonded Fibre Matrix
- Flexible Growth Medium
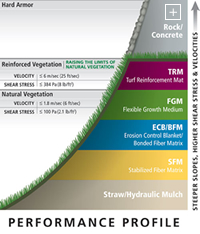
These categories of hydraulic mulches are arranged in order of increasing performance as can be seen in the diagram left.
The Four Products
Hydraulic Mulch
Hydraulic mulches (HMs) consist of shredded wood and/or paper fibres, water and/or a stabilizing emulsion. Stabilizing emulsions typically consist of an organic tackifier or an inorganic polymer. HMs are commonly used to aid in the establishment of vegetation and the temporary stabilization of flat surfaces and moderate slopes. HMs typically have a functional longevity of less than three months.
Stabilized Fibre Matrix
Stabilized Fibre Matrices (SM) consist of wood or paper fibres, stabilizing emulsions and water. Common stabilizing emulsions include cross-linked hydro-colloidal tackifiers and polyacrylamide flocculants.
Cross-linking is an important step in increasing the bond strength and longevity of the hydro-colloidal tackifier. Cross-linking is a chemical process that reduces the water solubility of the tackifier and, therefore, increases the longevity. Cross-linking also keeps the tackifier from rewetting and potentially leaching after the matrix has cured.
Bonded Fiber Matrix
Bonded Fiber Matrices (BFMs) have been in use for over 15 years and have received acceptance by many state departments of transportation, public agencies and private specifiers. BFMs are composed of thermally refined wood fibres, cross-linked hydro-colloidal tackifiers (10% by weight) and are 100% biodegradable. BFMs are designed to provide erosion protection for six to 12 months and are commonly used for erosion control and vegetative establishment on steep slopes, long slopes and highly erosive soils. Curing takes approximately 24 to 48 hours and application rates vary from 3,000-4,000 lb/ac based on slope length and inclination.
Flexible Growth Medium
Flexible Growth Mediums (FGMs) are composed of thermally refined wood fibres, cross-linked hydro-colloidal tackifiers (10% by weight), and crimped man-made fibres (5% by weight). The man-made fibres are crimped to interlock and provide mechanical reinforcement of the matrix. FGMs are the highest-performing hydraulically applied technology and provide greater than 99% erosion control effectiveness. They also require no curing period. The use of man-made fibres increases the loft of the matrix and thereby increases the porosity and water holding capacity. The increased water holding capacity has resulted in greater vegetative establishment. FGMs have functional longevities of greater than 12 months. FGMs are commonly used to stabilize steep slopes, long slopes, rough slopes, highly erosive soils and when rainfall is expected within 48 hours.
Hydraulic Technology Product Selection
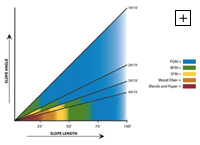
When selecting the appropriate hydraulically applied technology, three factors are evaluated:
- Functional Longevity
- Slope Length
- Slope Gradient
As the slope length and gradient increase, the water travels at a faster velocity, exerting larger erosive forces on the soil. Therefore, for steeper and longer slopes, a higher performing product is warranted to adequately stabilize the soil and increase factors of safety. Our trained staff at Hydroflex-EU will be happy to advise accordingly on the best product for your environment.
